|
A 38 year-old woman developed a severe and sudden headache followed by double vision and then loss of vision. |

![]()
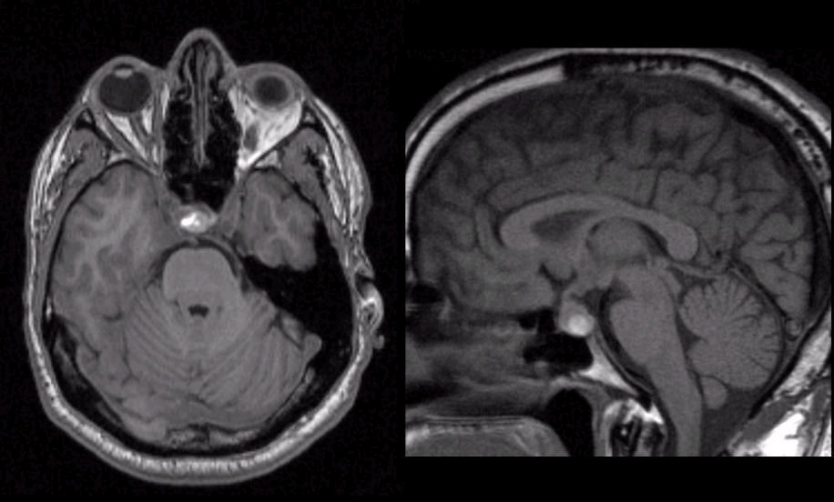
| Pituitary Apoplexy. (Left) T1-weighted axial MRI; (Right) T1-weighted
sagittal MRI. Note the enlargement of the pituitary gland. Also note
the bright signal within the
gland - this is subacute blood.
Pituitary apoplexy is a medical emergency that results from
hemorrhage into or infarction of the pituitary gland, typically
associated with a macroadenoma. Symptoms and signs
include the sudden onset of a severe headache (which can mimic
subarachnoid hemorrhage), altered mental status, visual symptoms,
and an acute hormonal withdrawal state. The visual symptoms result
from compression of the optic chiasm or optic nerves resulting in
visual field abnormalities or decreased visual acuity. The
extraocular muscles may also be impaired due to compression of
cranial nerves III, IV and VI that pass through the
cavernous sinus, adjacent to the sella. Treatment consists of
surgical decompression and urgent replacement of corticosteroids
to prevent vascular collapse. |
Revised
11/28/06.
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston