
![]()
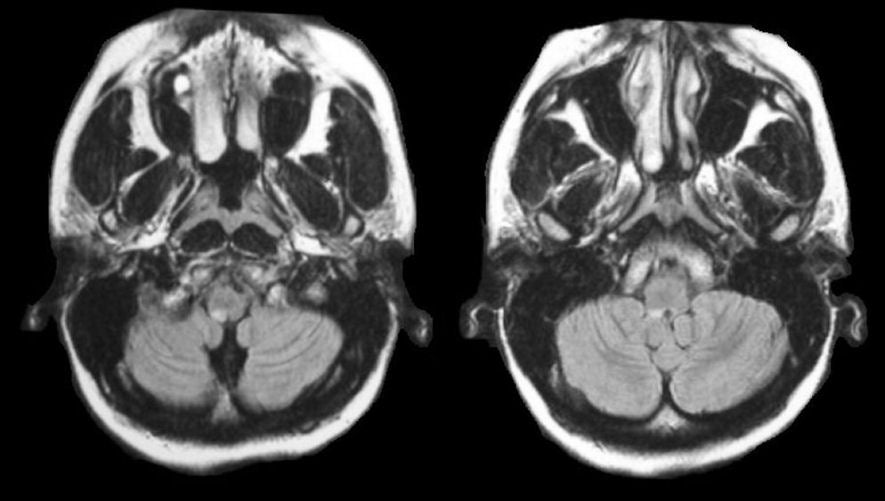
| Lateral Medullary Infarction: Flair axial MRI scans. Note the small area of infarction in the right lateral medulla. Strokes in the lateral medulla usually result from occlusion of the vertebral artery or posterior inferior cerebellar artery. A stroke in the lateral medulla results in a Wallenberg's syndrome, manifested by nausea, vomiting, and vertigo along with ipsilateral facial numbness, weakness of the ipsilateral soft palate, ipsilateral ataxia, and contralateral numbness of the body. An ipsilateral Horner's syndrome (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis) may be present. |
Revised
11/30/06
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston