|
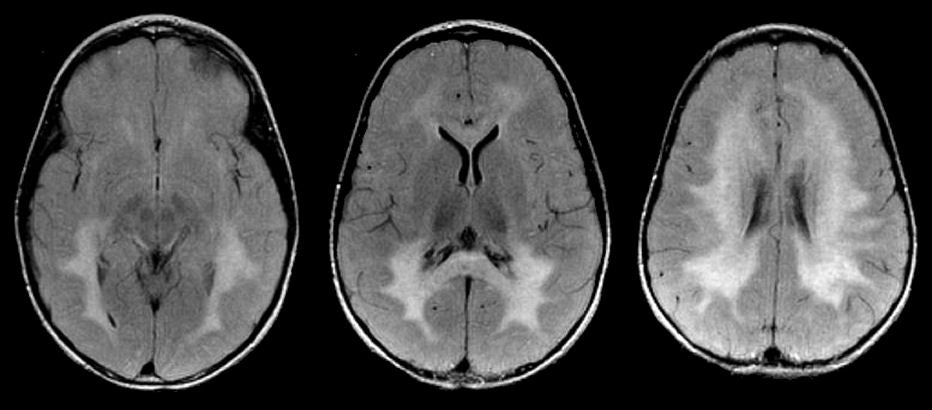
A 3 year-old girl presented with progressive spasticity, visual loss and loss of motor milestones. |

![]()
![]()
| Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD): Flair axial
MRI images. Note the bilateral confluent white matter
lesions, more prominent in the posterior areas. Also note the
involvement of the splenium of the corpus callosum. MLD is a disorder of central and peripheral myelin that results from the absence of the enzyme arylsulfatase A. The disorder may present at any age, although the majority of cases occur in the first two years of life. Polyneuropathy (weakness, hypotonia, depressed reflexes) with delayed motor milestones is a common early presentation. Severe cases may be confused with infantile spinal muscular atrophy. Later, hypotonia is replaced by spasticity and bilateral Babinski responses are present. Intellectual function deteriorates over time. MRI typically shows bilateral confluent white matter abnormalities. Similar white matter lesions can be seen in the other childhood leukodystrophies, including adrenoleukodystrophy, Krabbe disease, Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, Canavan disease, childhood ataxia with central hypomyelination (CACH or vanishing white matter disease). |
Revised
11/25/06
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston