|
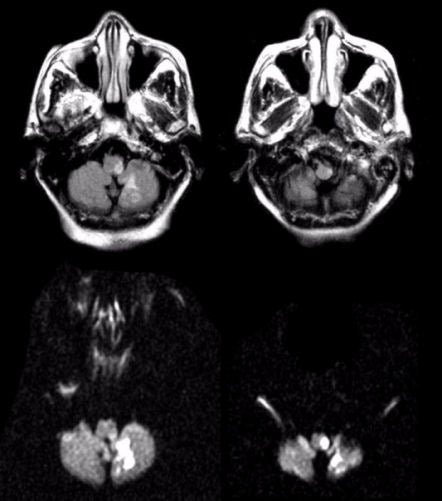
A 71 year-old woman presented with vertigo, nausea and vomiting. Examination showed a left sided Horner's syndrome, left facial numbness, left sided ataxia, weakness of the left soft palate, slurred speech, and numbness over the right side of the body. |

![]()
| Lateral Medullary and Inferior Cerebellar Infarction: (Top Left and Right) Flair axial MRIs of the lower medulla; (Bottom Left and Right) Corresponding diffusion-weighted MRI images of the top scans. Note the bright signal in the left lateral medulla and inferior cerebellum. This infarct is in the distribution of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA). Infarctions in the PICA territory result in a Wallenberg's syndrome: nausea, vomiting, and vertigo; ipsilateral facial numbness; weakness of the ipsilateral soft palate; ipsilateral ataxia; contralateral numbness of the body; and ipsilateral Horner's syndrome (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis). The abnormal diffusion weighted images indicate that the lesion is acute. |
Revised
11/29/06
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston