
![]()
![]()
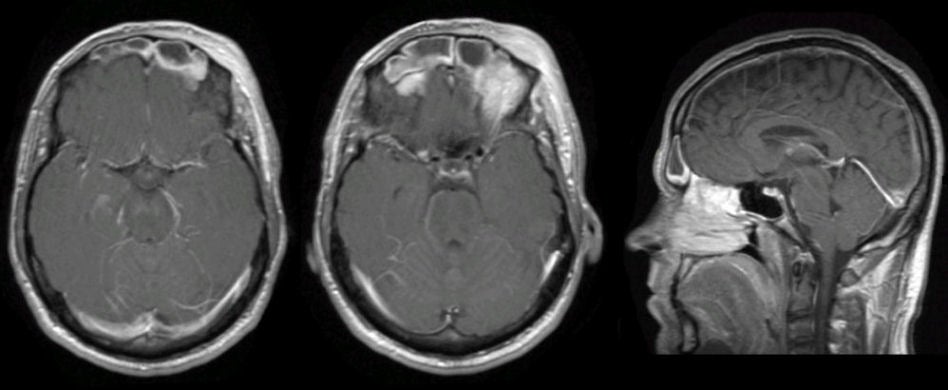
| Sinusitis and Epidural Abscess:
T1-weighted with gadolinium MRI scans; (Left and Middle) axial;
(Right) sagittal. Note the prominent
enhancement in the frontal sinuses, and erosion of bone into
the frontal lobes. Prompt surgical decompression
and aspiration of the purulent material was required, along with antibiotic
treatment.
Intracranial abscesses can occur in the epidural and subdural space as well as in the brain parenchyma. Infection most often occurs from spread through the blood system, or from direct invasion of an infection from an adjacent structure (e.g., sinusitis, otitis, mastoiditis, etc). Patients most often present subacutely over days to a few weeks with fever, headache, and/or focal neurological signs, including seizures. |
Revised
10/23/06
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston