
![]()
![]()
![]()
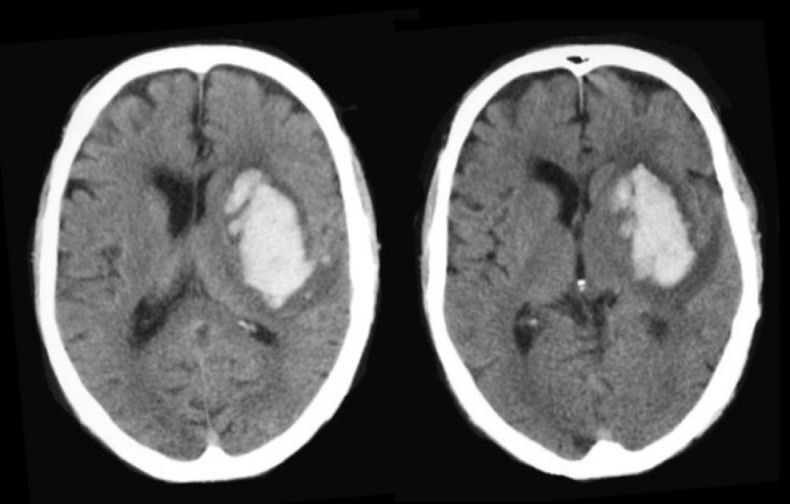
| Basal Ganglia (Putamen) Intracerebral Hemorrhage:
Axial CT scans. Note the large intracerebral hemorrhage originating in
the area of the basal ganglia on the left. The basal
ganglia is a common location for intracerebral bleeds due to hypertension. This is one of the common sites of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Hemorrhages in this location typically result in a contralateral hemiparesis affecting the face, arm and leg (from involvement of the internal capsule), associated with a hemisensory loss. With larger lesions, aphasia develops with lesions on the dominant side and neglect syndromes with lesions on the non-dominant side. With very large lesions, intracranial hypertension may develop, as manifested by headache, nausea and vomiting, and a depressed level of consciousness. |
Revised
11/15/06.
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston.