|
A 2 year-old boy underwent an evaluation for developmental delay. On examination, he had a mild right hemiparesis. |

![]()
![]()
![]()
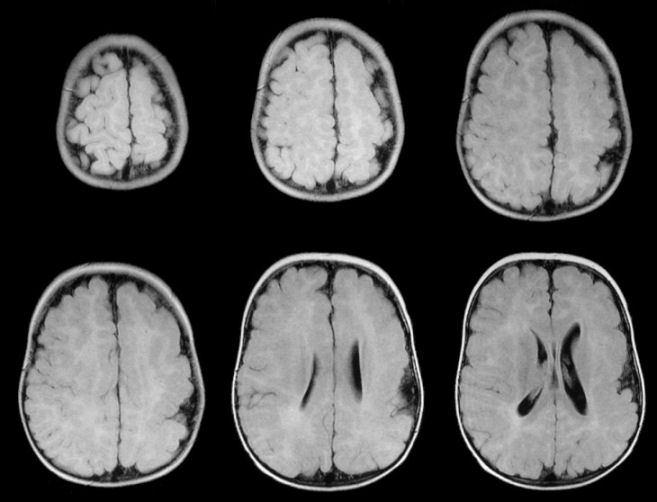
| Lissencephaly / Polymicrogyria / Pachygyria:
Flair axial MRIs. This patient displays several abnormalities
on the spectrum of neuronal migration disorders. If one looks
closely, one sees several areas wherein the gyri are abnormally small (polymicrogyria).
In addition, there are large areas completely devoid of sulci, known as either
pachygyria or macrogyria (thickened, large gyri). Note also the
asymmetry of the deformity - the left hemisphere is more abnormal,
likely the correlate of the patient's right sided weakness.
Neuronal migration disorders are a group of congenital disorders caused by impaired migration of neurons in the developing brain. Neuronal migration normally occurs during the second month of gestation. If the signals that guide neurons are impaired, a variety of structural defects may occur, including: • Lissencephaly In lissencephaly, there is a complete absence of gyri and sucli, with the surface of the brain appearing perfectly smooth. These children typically have severe mental retardation with microcephaly and seizures. Pachygyria is a milder variant of lissencephaly, characterized by a thickened cortex with large, broad gyri. |
Revised
11/18/06
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston