|
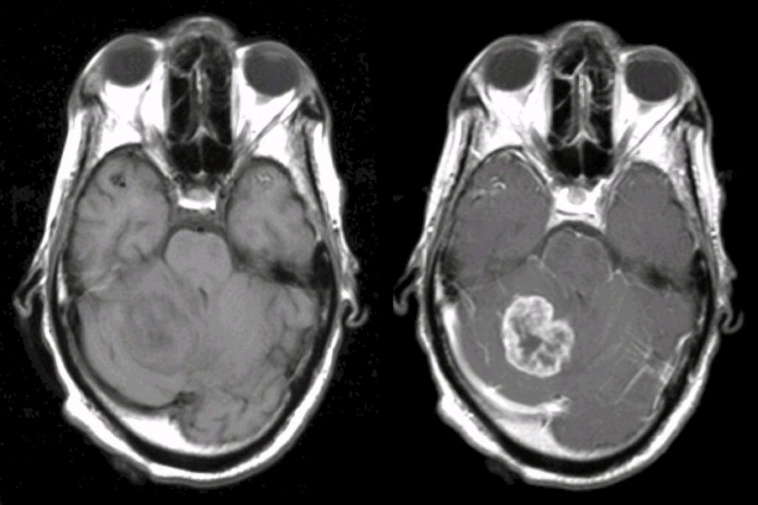
A 62 year-old man with known lung cancer presented with progressive headaches and an unsteady gait. |

![]()
![]()
| Metastatic Brain Tumor (Lung Cancer): (Left) T1-weighted
axial MRI; (Right) T1-weighted with gadolinium axial MRI. Note the
large enhancing tumor in the left cerebellum. Subsequent biopsy
demonstrated metastatic adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Metastatic disease from primary tumors elsewhere in the body account for
approximately 50% of all brain tumors. Metastases to the brain are nearly always
via the blood stream. They are typically found at the junctions between the gray
and white matter, which are highly vascular. Metastatic lesions commonly present
with focal or focal to generalized seizures or slowly progressive neurological
deficits. When the lesions become very large, signs and symptoms of increased
intracranial pressure develop (i.e., headache, lethargy, nausea and vomiting).
The most common primary tumors that metastasize to the brain are lung and
breast. Other tumors may also spread to the brain, including melanoma, lymphoma,
GI, and GU cancers. In some cases, it is the metastatic lesion in the brain, and
not the primary tumor, that brings the patient to medical attention. |
Revised
11/29/06.
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston