|
A 33 year-old man was brought to the hospital in coma following a head injury sustained during a motorcycle accident. |

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
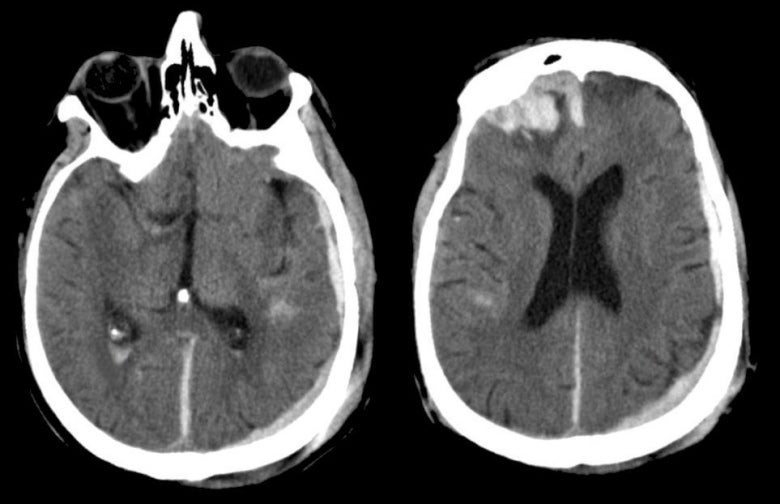
| Multiple Types of Hemorrhage.
Axial CT scans without contrast. Note
that there are three different types of hemorrhage in the same
patient: subdural hematoma, intraparenchymal hemorrhage (from
contusion), and intraventricular blood. Subdural hematomas are
recognized by their crescent shape overlying and compressing the
brain. They are arbitrarily divided into three types: acute (< 4
days), subacute (4-21 days) and chronic (> 21 days). Traumatic
contusions consist of hemorrhage and surrounding edema. The frontal
poles and the temporal lobe tip are the most common locations for
cerebral contusions following head injury, wherein the brain
continues to move forward, striking the inner skull, after the head
has stopped moving. Note the intraventricular hemorrhage with the
layering of blood in the ventricles. In this case, the
intraventricular hemorrhage occurred in the setting of traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage
and diffusion of blood into the ventricles. In the acute stage, blood is bright on CT. Eventually in the chronic state, the blood turns dark. In the subacute stage, a variety of patterns can be seen. Axial CT scans of the brain. Note that there are several different types of hemorrhage in the same patient: a frontal contusion; subdural hematomas; parietal/temporal contusions; and intraventricular blood. |
Revised
11/22/06.
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston