|
A 52 year-old man with poorly controlled hypertension developed acute lethargy and bilateral leg weakness. |

![]()
![]()
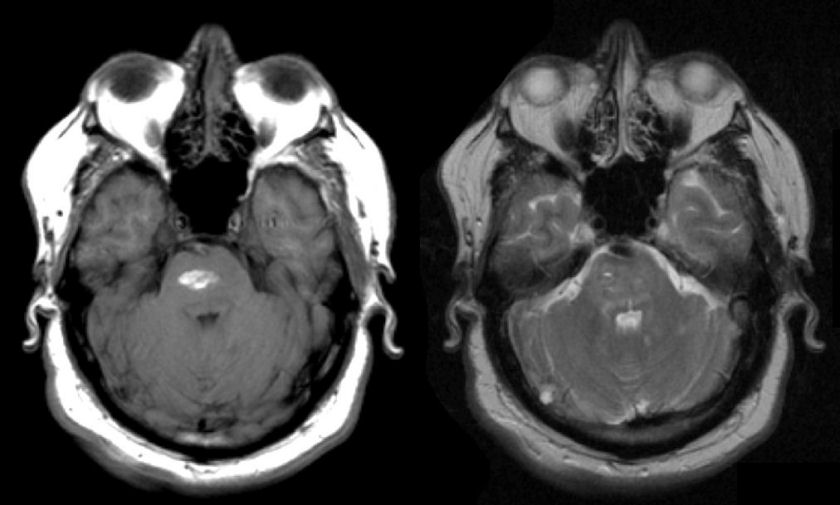
| Pontine Intracerebral Hemorrhage: (Left) T1-weighted
axial MRI;
(Right) T2-weighted axial MRI. Note the bright signal in the basis pontis on the T1-weighted
image (signifying methemoglobin) and the mixed signal on the T2-weighted
image. This is the MRI appearance of a subacute intracerebral hemorrhage.
The pons is a classic location for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Because of the location of the hemorrhage, the patient is lethargic (involvement of the ascending reticular activating system), has no horizontal eye movements (involvement of the horizontal eye movement centers) and is paraplegic (involvement of the basis pontis). Prognosis in these cases is usually grim. |
Revised
11/23/06.
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston