Deep-learning network possible step toward automating biopsy slide analysis
A deep-learning computer network developed through research led by Case Western Reserve University was 100 percent accurate in determining whether invasive forms of breast cancer were present in whole biopsy slides. Looking closer, the network correctly made the same determination in each individual pixel of the slide 97 percent of the time, rendering near-exact delineations of the tumors. Compared to the analyses of four pathologists, the machine was more consistent and accurate, in many cases improving on their delineations. In a field where time and accuracy can be critical to a patient’s long-term prognosis, the study is a step toward automating part of biopsy analysis and improving the efficiency of the process, the researchers say. Currently, cancer is present in one in 10 biopsies ordered by physicians, but all must be analyzed by pathologists to identify the extent and volume of the disease, determine if it has spread and whether the patient has an aggressive or indolent cancer and needs chemotherapy or a less drastic treatment. Last month, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved software that allows pathologists to review biopsy slides digitally to make diagnosis, rather than viewing the tissue under a microscope. “If the network can tell which patients have cancer and which do not, this technology can serve as triage for the pathologist, freeing their time to concentrate on the cancer patients,” said Anant Madabhushi, F. Alex Nason professor II of biomedical engineering at Case Western Reserve and co-author of the study detailing the network approach, published in Scientific Reports.The study
To train the deep-learning network, the researchers downloaded 400 biopsy images from multiple hospitals. Each slide was approximately 50,000 x 50,000 pixels. The computer navigated through or rectified the inconsistencies of different scanners, staining processes and protocols used by each site, to identify features in cancer versus the rest of the tissue. The researchers then presented the network with 200 images from The Cancer Genome Atlas and University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center. The network scored 100 percent on determining the presence or absence of cancer on whole slides and nearly as high per pixel.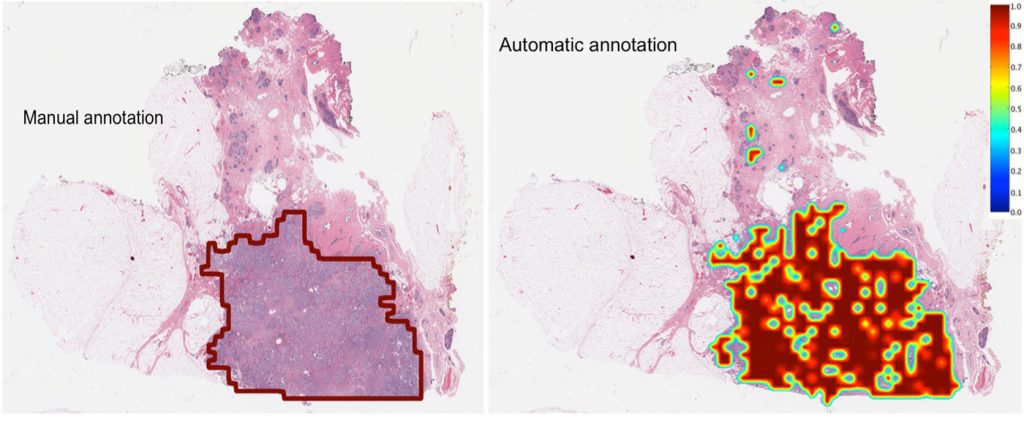 A deem-learning network was able to not only detect the presence of aggressive breast cancers but, in many cases, improved the delineated boundaries of tumors compared to those drawn by pathologists.
“The network was really good at identifying the cancers, but it will take time to get up to 20 years of practice and training of a pathologist to identify complex cases and mimics, such as adenosis,” said Madabhushi, who also directs the Center of Computational Imaging and Personalized Diagnostics at Case Western Reserve.
Network training took about two weeks, and identifying the presence and exact location of cancer in the 200 slides took about 20 to 25 minutes each.
That was done two years ago. Madabhushi suspects training now—with new computer architecture—would take less than a day, and cancer identification and delineation could be done in less than a minute per slide.
“To put this in perspective,” Madabhushi said, “the machine could do the analysis during ‘off hours,’ possibly running the analysis during the night and providing the results ready for review by the pathologist when she/he were to come into the office in the morning.”
Madabhushi worked with Angel Cruz-Roa, a PhD student, and Fabio Gonzalez, professor, Department of Systems and Industrial Engineering at the Universidad Nacional de Colombia, in Bogota; Hannah Gilmore, associate professor of pathology at Case Western Reserve School of Medicine; Ajay Basavanhally of Inspirata Inc., Tampa Florida; Michael Feldman, professor of pathology and laboratory medicine, and Natalie Shi, of the Department of Pathology, at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania; Shridar Ganesan, associate professor of medicine and pharmacology at the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey; and John Tomaszewski, chair of pathology and anatomical services at the University of Buffalo, State University of New York.
Much of the study was built on research by Madabhushi and Andrew Janowczyk, a biomedical engineering Postdoctoral Fellow at Case Western Reserve. They led development of what they termed “a resolution adaptive deep hierarchical learning scheme,” which can cut the time for image analysis using deep learning approaches by 85 percent.
Deep-learning networks learned to identify indicators of cancer at lower resolutions to determine where further analysis at high levels of magnification, and thus greater computation time, were necessary to provide precise results. In short, the scheme eliminated time-consuming, high-resolution analysis of healthy tissue.
To manage the variance in staining of digitized biopsy images that can confound computer analysis, the researchers developed a technique called Stain Normalization using Sparse AutoEncoders. The technique partitions images into tissue sub-types so color standardization for each can be performed independently.
To speed research in the field, Janowczyk and Madabhushi also published a tutorial on deep learning for digital pathology image analysis. The paper was recently awarded the most cited paper award from the Journal of Pathology Informatics.
This article was originally published May 10, 2017.
A deem-learning network was able to not only detect the presence of aggressive breast cancers but, in many cases, improved the delineated boundaries of tumors compared to those drawn by pathologists.
“The network was really good at identifying the cancers, but it will take time to get up to 20 years of practice and training of a pathologist to identify complex cases and mimics, such as adenosis,” said Madabhushi, who also directs the Center of Computational Imaging and Personalized Diagnostics at Case Western Reserve.
Network training took about two weeks, and identifying the presence and exact location of cancer in the 200 slides took about 20 to 25 minutes each.
That was done two years ago. Madabhushi suspects training now—with new computer architecture—would take less than a day, and cancer identification and delineation could be done in less than a minute per slide.
“To put this in perspective,” Madabhushi said, “the machine could do the analysis during ‘off hours,’ possibly running the analysis during the night and providing the results ready for review by the pathologist when she/he were to come into the office in the morning.”
Madabhushi worked with Angel Cruz-Roa, a PhD student, and Fabio Gonzalez, professor, Department of Systems and Industrial Engineering at the Universidad Nacional de Colombia, in Bogota; Hannah Gilmore, associate professor of pathology at Case Western Reserve School of Medicine; Ajay Basavanhally of Inspirata Inc., Tampa Florida; Michael Feldman, professor of pathology and laboratory medicine, and Natalie Shi, of the Department of Pathology, at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania; Shridar Ganesan, associate professor of medicine and pharmacology at the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey; and John Tomaszewski, chair of pathology and anatomical services at the University of Buffalo, State University of New York.
Much of the study was built on research by Madabhushi and Andrew Janowczyk, a biomedical engineering Postdoctoral Fellow at Case Western Reserve. They led development of what they termed “a resolution adaptive deep hierarchical learning scheme,” which can cut the time for image analysis using deep learning approaches by 85 percent.
Deep-learning networks learned to identify indicators of cancer at lower resolutions to determine where further analysis at high levels of magnification, and thus greater computation time, were necessary to provide precise results. In short, the scheme eliminated time-consuming, high-resolution analysis of healthy tissue.
To manage the variance in staining of digitized biopsy images that can confound computer analysis, the researchers developed a technique called Stain Normalization using Sparse AutoEncoders. The technique partitions images into tissue sub-types so color standardization for each can be performed independently.
To speed research in the field, Janowczyk and Madabhushi also published a tutorial on deep learning for digital pathology image analysis. The paper was recently awarded the most cited paper award from the Journal of Pathology Informatics.
This article was originally published May 10, 2017.