2023
Mesenchymal Wnts are required for morphogenetic movements of calvarial osteoblasts during apical expansion.
Polsani N, Yung T, Thomas E, Phung-Rojas M, Gupta I, Denker J, Feng X, Ibarra B, Hopyan S, Atit RP. bioRxiv. 2023 Dec 7:2023.12.05.570300. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.05.570300. Preprint.
During apical expansion of the frontal bone primordia, non-canonical Wnts in the mesenchyme are required for morphogenetic movements of calvarial osteoblasts, cell elongation, cell polarity, and protrusive activity. We found calvarial osteoblasts have convergent extension behavior in the basal portion of the primordia and protrusive activity more apically that is dependent on non-canonical Wnt signaling.
Apical expansion of calvarial osteoblasts and suture patency is dependent on graded fibronectin cues.
Feng X, Molteni H, Gregory M, Lanza J, Polsani N, Wyetzner R, Hawkins MB, Holmes G, Hopyan S, Harris MP, Atit RP.bioRxiv. 2023 Jan 16:2023.01.16.524278. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.16.524278. Preprint.
Apical expansion of frontal bone primordia is dependent on graded expression of Fibronectin1 matrix protein. Fibronectin1 substrate also promotes cellular elongation, actin enrichment and preserves suture patency of the coronal suture. Calvarial osteoblasts use Wasl-dependent lamellipodia to migrate on Fibronectin1 substrate during apical expansion.
2021
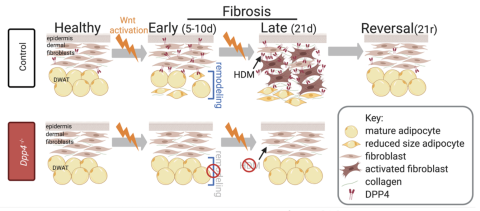
Skin fibrosis and recovery is dependent on Wnt activation via DPP4
Jussila AR, Zhang B, Caves E, Kirti S, Steele M, Hamburg-Shields E, Lydon J, Ying Y, Lafyatis R, Rajagopalan S, Horsley V, Atit RP. Skin fibrosis and recovery is dependent on Wnt activation via DPP4, The Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2021), doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/
Upon Wnt activation in the dermis and dermal white adipose tissue (DWAT), there is depletion of lipid filled adipocytes by 10days and increase in high density matrix and fiber thickness of collagen matrix and proteoglycans by 21 days. Upon de-inducing Wnt activation, there is spontaneous reversal of fibrotic remodeling in dermis and DWAT. In the absence of Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4), the dermis and DWAT are rescued from Wnt activated fibrotic remodeling. This protection leads to preservation of skin architecture.
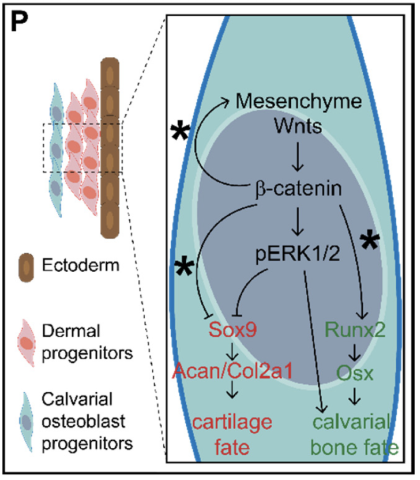
Wnt-Dependent Activation of ERK Mediates Repression of Chondrocyte Fate during Calvarial Development
Ibarra BA, Machen C, Atit RP. Wnt-Dependent Activation of ERK Mediates Repression of Chondrocyte Fate during Calvarial Development. J Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 27;9(3):23. doi: 10.3390/jdb9030023.
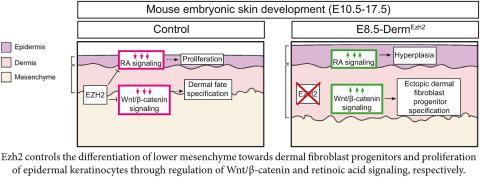
Dermal EZH2 orchestrates dermal differentiation and epidermal proliferation during murine skin development
Thulabandu V, Nehila T, Ferguson JW, Atit RP. Dermal EZH2 orchestrates dermal differentiation and epidermal proliferation during murine skin development. Dev Biol. 2021 Oct;478:25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.06.008. Epub 2021 Jun 21. PMID: 34166654
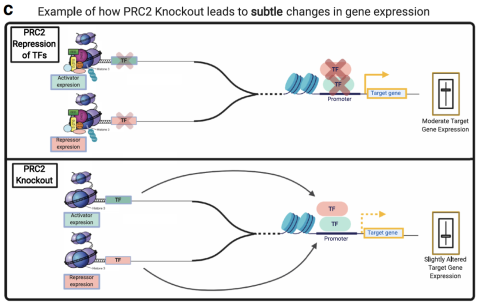
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2: a Dimmer Switch of Gene Regulation in Calvarial Bone Development
Nehila T, Ferguson JW, Atit RP. Polycomb Repressive Complex 2: a Dimmer Switch of Gene Regulation in Calvarial Bone Development. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020 Aug;18(4):378-387. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00603-5.PMID: 32748325 Review.
2019-2020
- Ibarra BA, Atit RP. What Do Animal Models Teach Us About Congenital Craniofacial Defects? Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1236:137-155. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-2389-2_6.
- Sun Q, Lee W, Mohri Y, Takeo M, Lim CH, Xu X, Myung P, Atit RP, Taketo MM, Moubarak RS, Schober M, Osman I, Gay DL, Saur D, Nishimura EK, Ito M. A novel mouse model demonstrates that oncogenic melanocyte stem cells engender melanoma resembling human disease. Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 4;10(1):5023. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12733-1.
- Tao, H., Zhu, M., Lau, K., Whitley, O., Samani, M., Xiao, X., Chen,X.X., Hahn, N.A., Liu, W., Valencia, M., Wu, M., Wang, X., Fenelon, K.D., Pasiliao, C.C., Hu, D., Wu, J., Spring, S., Ferguson, J.W., Karuana, E.P., Henkelman, R.M., Dunn, A., Huang, H., Hsin-Yi Henry Ho, H-Y.H., Atit, R.P., Goyal, S., Sun, Y., Hopyan S. (2019). Oscillatory cortical forces promote three dimensional cell intercalations that shape the mandibular arch. Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 12;10(1):1703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09540-z.
- DiNuoscio G., Atit RP. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the mouse embryonic cranial mesenchyme is required to sustain the emerging differentiated meningeal layers. Genesis 2019. Jan;57(1); e23279. doi:10.1002/dvg.23279
2018
- Ferguson J, Devarajan M, DiNuoscio G, Saiakhova A, Liu CF, Lefebvre V, Scacheri P, Atit RP. PRC2 is Dispensable in Vivo for β-Catenin-Mediated Repression of Chondrogenesis in Mouse Embryonic Cranial Mesenchyme. G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Dec 9. (Epub ahead of print).
- Ferguson JW, Devarajan M, Atit RP. Stage-specific roles of Ezh2 and Retinoic acid signaling ensure calvarial bone lineage commitment. Dev Biol. 2018 Nov 15;443(2):173-187.
- Ferguson JW, Atit RP. A tale of two cities: The genetic mechanisms governing calvarial bone development. Genesis. 2018 Aug 28:e23246. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23248. Review.
2016-2017
- Mullin NK, Mallipeddi NV, Hamburg-Shields E, Ibarra B, Khalil AM, Atit RP.Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway Regulates Specific lncRNAs That Impact Dermal Fibroblasts and Skin Fibrosis. 2017, Frontiers Genetics. Nov 21:8.
- Budnick I, Hamburg-Shields E, Chen, D., Torre, E, Jarrell A., Akhtar-Zaidi B, Cordovan O, Spitale RC, Scacheri PC, Atit RP. (2016). Defining the identity of mouse embryonic dermal fibroblasts. genesis: Journal of Genetics and Development 2016 Aug;54(8):415-30.
- Xiao Y, Thoresen DT, Williams JS, Atit RP, Wong SY, Brownell I. (2016). Sonic hedgehog signaling is essential for touch dome Merkel cell development. PLoS Genetics, 12 (7):e1006150.
- Goodnough LH, DiNuoscio GJ, Atit RP (2016). Twist1 contributes to cranial bone initiation and dermal condensation by maintaining Wnt signaling responsiveness. Developmental Dynamics. Feb;245(2):144-56.
2015
- Hamburg-Shields E, DiNuoscio GJ, Mullin NK, Lafayatis R, Atit RP (2015). Sustained beta-catenin activity in dermal fibroblasts promotes fibrosis by up-regulating expression of matrix protein-coding genes. J of Pathology, 235, p686-97.
- Goodnough, L.H. DiNuoscio, G, Ferguson, J.W., Williams T., Lang R.A., and Atit RP (2014). Distinct requirements for cranial ectoderm and mesenchyme-derived Wnts in specification and differentiation of osteoblast and dermal progenitors. PLoS Genetics, 10, e1004152.
2012
- Goodnough LH, Chang AT, Treloar C, Yang J, Scacheri PC, Radhika Atit.(2012). Twist1 mediates repression of chondrogenesis by β-catenin to promote cranial bone progenitor specification. Development, 139, p. 4428-38.
- Myung PS, Takeo M, Ito M, Radhika Atit.(2012). Epithelial Wnt ligand secretion is required for adult hair follicle growth and regeneration. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 133, p31-41.
- Emily Hamburg and Radhika Atit (2012). Sustained beta-catenin activity in dermal fibroblasts is sufficient for skin fibrosis, Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 132, p2469-72.
- Demeng Chen, Andrew Jarrell, Canting Guo, Richard Lang, Radhika Atit (2012). Dermal beta-catenin in response to ectodermal Wnt ligands are required for fibroblast proliferation and hair follicle initiation, Development, 139: 1522-33.
- Jun Wei, F. Fang, Ann P. Lam, J.L. Sargent, Emily Hamburg, M.E. Hinchcliff, C. Gottardi, Radhika Atit, M.L. Whitfield, J. Varga (2012). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is hyperactived in systemic sclerosis and induces smad-dependent fibrotic responses in mesenchymal cells, Arthritis and Rheumatism, 64, p2734-45.
2010
- Thu Tran, Andrew Jarrell, Gabriel Zentner, Isaac Brownell, Peter Scacheri, Radhika Atit (2010). Role of canonical Wnt signaling/beta-catenin in cranial dermal development, Development, 137: 3973-84.
- Preethi Mani, Andrew Jarrell, John Myers, Radhika Atit (2010). Visualizing canonical Wnt signaling during mouse craniofacial development. Developmental Dynamics, 239:354-63.
2003-2008
- Knothe Tate, ML; Falls, TD; McBride, SH; Atit, R., Knothe, UR (2008). Mechanical modulation of osteochondroprogenitor cell fate. Int. J. Biochem Cell Biol. 40 (12): 27020-38. (Review).
- Jennifer Ohtola, John Myers, Batool Akhtar-Zaidi, Diana Zuzindlak, Pooja Sandesara, Karen Yeh, Susan Mackem, and Radhika Atit (2008). Beta-Catenin has sequential roles in the survival and specification of ventral dermis. Development 135:2321-2329.
- Liu F, Chu EY, Watt B, Zhang Y, Gallant NM, Andl T, Yang SH, Lu MM, Piccolo S, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Taketo MM, Morrisey EE, Atit R, Dlugosz AA, Millar SE. (2008). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling directs multiple stages of tooth morphogenesis. Developmental Biology 313 p210-24
- Atit R., Sgaier, S. Mohammed, O., Taketo, M., Dufort, D., Joyner, A., Niswander, L., Conlon, R. (2006). Beta-catenin activity is necessary and sufficient for dorsal dermal fate specification. in mouse. Developmental Biology, 296, p164-176.
- Atit, R. , Conlon, R, and Niswander, L. (2003). EGFR signaling patterns the feather array by promoting interbud fate. Developmental Cell 4 p231-40