Make: PROFLUIDICS 285D (CADWorks3D)
Details
CADWorks3D printer ProFluidics 285D is a high-end DLP printer with 4 million pixel projector technology and a build size of 100x62x120mm. Its distinguishing feature is dynamic pixel advantage which allows the printer to reliably achieve an XY pixel resolution of 28.5um; it is able to take the cube-like structure that is prevalent with DLP prints and find the best curve to fit to create a smoother, rounded-out surface finish.
Small
Make: Sprout Plus Mini (Heathrow Scientific)
Details:
- Maximum capacity: 6 x 1.5/2.0, 0.5, 0.2 mL
- Maximum speed: Appro. 6,000 rpm (fully loaded)
- Maximum RCF: 2000 x g
Medium
Make: Sorvall Legend Micro 21 Microcentrifuge (ThermoFisher)
Details:
- Maximum capacity: 24 x 1.5/2.0 mL
- Maximum speed: 14800 rpm
- Maximum RCF: 21100 x g
- Temperature Range: Set from -9 °C to +40 °C per 1 °C increment
Large
Make: Sorvall ST 8 Small Benchtop Centrifuge (ThermoFisher)
Details:
- Maximum capacity: 6 × 50 mL
- Maximum speed: 16000 rpm
- Maximum RCF: 24328 × g
Make: Dell Desktop Computers
Details:
- Intel CPUs with 4 cores & 8 threads
- 32 GB DDR4 memory
- 1 TB NVMe solid-state driver
- 2 TB hard driver
Workstations are used to run simulations (MATLAB or Python), SolidWorks (CAD), SigmaPlot, imageJ, or any other desired software.
If supercomputing power is needed, our lab collaborates with the Ohio supercomputer facility, Ohio Supercomputer Center, to use their high-performance computing, advanced cyberinfrastructure, and other computational science education services.
Make: Arium Mini (Sartorius)
Details:
- Resistivity: 18.2 Mohm.cm at 25°C
- Feedwater Source: Distilled, DI, RO, EDI
- Volume dispensed from 50mL
Deionized water is used extensively in studying chemical reactions, colloidal interaction, and biological sample preparation. Deionization systems work by replacing negative and positive molecules in the water with H+ and OH- molecules. Organic substances are removed through filtration which improves the quality of the water and prevents the formation of scale deposits.
Make: Byko-drive S Automatic Film Applicator (Gardco)
Details:
- Drawdown speed can be set to 10 mm/s or 1 inch/s
- The film casting knife allows for Gap Clearance: 0-3.8 mm and has a blade Width: 2 inches
This machine can be used for applying liquid films onto any substrates with desired chemistry/composition. It is useful for studies involving liquid surface analysis where the applied film thickness is known.
Make: Isotemp (Fisherbrand)
Details: Temperature range: 50° – 250 °C
Ovens are used for sample drying, baking, aging tests, glassware drying, dry sterilization and processing electronics.
Make: FASTCAM Mini AX (Photron)
Details:
- 1024 x 1024 pixels at 2,000 fps
- Max frame rate: 170,000 fps
A high-speed camera can capture images with exposures of less than 1/1000 second or frame rates in excess of 250 fps. It is used for recording fast-moving objects as photographic images onto a storage medium. The recorded images can be played back in slow motion to study the short-time dynamics in an experiment such as fast-moving particles in a microfluidic channel, spray droplets in the air, impact of a drop on a surface, etc.
Snapshot of the result:
Capturing dynamics of a droplet as it impacts the substrate and deforms before achieving equilibrium shape
Make: T-25 Ultra Turrax (IKA)
Details:
- Handle sample volumes from 0.001 to 2 litres
- System can be used with tough solids or large volume samples
This instrument is useful for batch homogenizing of cell tissues, emulsifying suspended solids, and air pollution filter extraction. A rotor within a stainless-steel shaft acts as a centrifugal pump to recirculate the liquid and suspended solids through a generator, where shear, impact, collision, and cavitation provide rapid homogenization.
Make: Thorlabs
Details:
- CMOS Camera & High-Magnification Zoom Lens (12×, Thorlabs)
- Cuvette holder with water jacket for temperature control
- White light illuminator
- Software for capturing images
CMOS camera is attached with a 12× magnification zoom lens to capture the change in height of the particle suspension in the cuvette during the sedimentation process. The zoom lens setup also has a coaxial illumination port, that allows capturing the images by the front illumination mode. A cuvette mount made of aluminum with channels for water circulation is used for temperature control of the sample.
Snapshot of the result:
Make: IXplore Standard
Details:
- Observation Method: Brightfield, Fluorescence (Blue/Green Excitation)
- Illuminator: 100 W Halogen Lamp
- Objective: 4 – 40 × (Nikon)
- Camera: Kiralux 5.0 MP CMOS Camera (Thorlabs)
- Microscope stage with temperature control
Microscopes are useful in investigating structures, material flow, organic and inorganic particles within a range of 10-7 – 10-3 m. Combining the microscope with a camera allows capturing the dynamics of particle flow or rearrangements. Inverted microscopes are especially useful in studying samples at the bottom of a large container or where space above the specimen is required for micromanipulator tools. They are also extremely useful in studying flows in microfluidic channels and microreactors.
Snapshot of the result:
3 µm Janus spheres consisting of Platinum patch on polystyrene beads suspended in water – H2O2 mixture
Make: BX51 WI (Olympus)
Details:
- Includes 690 nm dichroic mirror
- Fluorescence light is sent to the front port, and IR-DIC light is sent to the back port allowing two cameras to image simultaneously with no vibration introduced by light path selection
- IR-DIC observation is compatible with 775 nm and 900 nm wavelengths
- 4 - 40× objective lens options available
- Can be coupled with Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) setup
- Digital CMOS camera (ORCA-Fusion, C14440-20UP, Hamamatsu) - 2304 × 2304 px (5.3 Megapixels), 100 frames/s (at 2304 × 2048 px ROI)
Microscopes are useful in investigating structures, material flow, organic and inorganic particles within a range of 10-7 – 10-3 m. Combining the microscope with a camera allows capturing the dynamics of particle flow or rearrangements. Upright microscope with fluorescence filters allows capturing fluorescently labelled samples excited at different wavelengths of light. The application of an array of fluorochromes makes it possible to identify microscopic particles with a high degree of specificity amid non-fluorescing medium.
Snapshot of the result:
Make: Accumet AB 200 (Fisherbrand)
Details:
- Measures pH, conductivity, TDS (total dissolved solids), salinity and resistivity
- pH Range: -2.000 to 20.000 pH
- Conductivity Range: 0.00μS to 500.0mS
- mV Range: ±2000.0mV
- TDS Range: 0.00ppm to 500 ppt (TDS factor 1.00)
- Salinity Range: 0 to 80.0 ppt
- Resistivity Range: 2.000 Ohm to 20.0 MOhm
pH meter is used to measure the hydrogen ion conductivity in an aqueous solution that reveals the acidity or alkalinity of the medium. The measure of acidity or alkalinity is expressed in values of pH which is critical information in many chemical and biological studies. In addition, this instrument allows measurement of ionic conductivity which is useful information for studying electrolytes that ubiquitous in colloidal systems.
Make: Tergeo (Pie Scientific)
Details:
- Cleaning modes: Direct mode and downstream mode. Dual plasma sources for the two plasma cleaning modes. Direct mode plasma cleaning for high-speed etching and surface modification; remote/downstream mode plasma cleaning for gentle surface contamination removal, such as SEM/TEM sample cleaning
- Continuous and pulsed plasma. Pulse ration can be changed from 100% (continuous) to less than 1%
- Sample shelf: 2mm thick high purity quartz plate
Plasma is ionized gas that consists of ions, electrons and neutral atoms. It is the fourth state of matter, and it could be used to treat/modify an array of materials along with surfaces with complex geometries. A plasma cleaning system allows the efficient cleaning of a surface without having a negative impact on other properties of the surface. A plasma cleaning system works with chemical functional groups, and results in rendering most surfaces hydrophilic.
Applications:
1. SEM/TEM sample cleaning for carbonaceous contamination removal and oxide reduction
2. Surface treat before biomedical coating and improve hydrophilicity of medical implants
3. Optics, glass and substrate cleaning before epoxy bonding
4. Photoresist ashing, descum and silicon wafer cleaning
5. PDMS, microfluidics, glass slides and lab-on-a-chip
6. Improve bonding for materials
Name: Modular Compact Rheometer 702e Space Multidrive
Make: Anton Paar
Details:
-
Torque range from 0.5 nNm to 230 mNm.
-
Measuring geometries: Cone and plate (50 mm dia.), parallel plate (50 mm dia.), roughened parallel plate(25 mm dia.).
-
Equipped with peltier-temperature-controlled device (PTD) with active heating and cooling from -50 °C to +220 °C.
-
Suitable for combination with additional instruments, e.g., a confocal microscope.
Picture:
Short description:
The highly sensitive air-bearing-supported rotational drive is capable of sensing normal force with a resolution of 0.5 mN. Parallel plate and cone and plate measuring geometries allow characterization of a wide range of materials from low viscosity Newtonian liquids to viscoelastic pastes and gels. A peltier-temperature controlled device enables rheological measurements over a wide range of temperature from -50 to 220 0C. The instrument can also be coupled with microscopes to obtain direct correlation between microstructure of a material and its rheological behavior.
Make: Custom
- Digital air-cooled CCD camera (Hamamatsu ORCA-R2)
- Upright microscope system (Olympus BX51WI)
- 40× microscope objective (LUCPLFLN40X, NA = 0.6, Olympus)
- 633 nm laser (PLM-633.0-PMF, NECSEL Co.)
- Aspherical collimator (CFC-8X-A, f = 7.5 mm, Thorlabs), linear polarizer (FBR-LPVIS 500–720 nm, Thorlabs)
- Custom-made trapezoidal prism (BK7 glass, width: 25 mm, length: 50 mm at the larger facet)
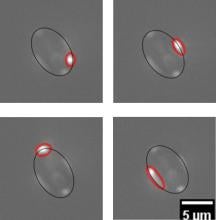
SMR-TIRM is currently being developed as a variant of classic TIRM to measure the ~kT scale interactions of micrometer scale anisotropic particles in close proximity to a boundary. In classic TIRM, a particle’s position relative to the neighboring boundary is inferred from the integrated scattered light intensity, whereas SMR-TIRM uses the morphology of scattered light to infer position and orientation. Current projects in our lab focus on (1) mapping experiments to obtain scattering morphology from model systems and (2) measuring the adhesion and deposition of particles.
Snapshot of the result:
The scattering light morphology from polystyrene ellipsoids at different azimuthal angles. The black line shows the outline of the ellipsoid particle, the red line shows the morphology of scattered light.
Publications:
- Scattering Morphology Resolved Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (SMR-TIRM) of Colloidal Spheres. J Yan, D Efremenko, AA Vasilyeva, A Doicu, T Wriedt, and CL Wirth, accepted in Computational Mathematics and Modeling (2021): 1-8.
- Developing scattering morphology resolved Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (SMR-TIRM) for orientation detection of colloidal ellipsoids. A Rashidi, S Domínguez-Medina, J Yan, DS Efremenko, AA Vasilyeva, A Doicu, T Wriedt, CL Wirth, Langmuir (2020)
- A light scattering model for total internal reflection microscopy of geometrically anisotropic particles., A Doicu, A A Vasilyeva, Dmitry S Efremenko, C L Wirth and T Wriedt, Journal of Modern Optics (2019)
Make: Spin Coater (Ossila)
Details:
- Spin speeds: 120 to 6000 rpm
- Different spin coating conditions - from slow dry crystallization to ultra-thin films
- Size of substrate: 25.4 x 25.4 x 1 mm
A spin coating cycle consists of four key stages: material deposition on substrate, spin up, spin off, and evaporation. First, the desired solution is cast onto the substrate using a pipette. Then, during the spin up and spin off stages, the solution is pushed outwards by the centripetal force and spreads up to cover the substrate. Most of the excess solution is expelled to the side of the substrate and airflow allows for the film to dry as it spins. Finally, in the evaporation stage, the solvent evaporates to leave a thin, uniform film behind.
Make: ATR206C1, Atria Series (ThorLabs)
Short description: Principle of operation
SS-OCT technology measures the magnitude and time delay of reflected light in order to construct depth profiles (A-scans) of the sample being imaged. Adjacent A-scans are then synthesized to create an image.
Swept laser source tunes the lasing wavelength over a broad wavelength range, at hundreds of kilohertz repetition rate and allow the sample depth profile measurements at high sweeping rates of the laser. The interference signals from the sample are collected using a high efficiency balanced detection scheme. Each sweep of the laser wavelength provides a depth scan at a sample surface point that yields a depth dependent reflectivity profile along the direction of the laser illumination path.
For more in-depth understanding on OCT, refer to A. F. Fercher et al., 2003, Rep. Prog. Phys., 66, 239.
Snapshot of result:
Make: Pump 11, Pico Plus Elite (Harvard Apparatus)
Details:
- Syringes used range from 0.5 µl – 10 ml
- 0.54 pl/min to 11.70 ml/min
Syringe pumps are devices that provide a continuous flow in a microfluidic channel or a microreactor by pumping fluid from a syringe at a constant flow rate. Multiple syringes with same or different fluids can be used in parallel for higher flow rates or mixing/reacting in a microreactor. The pump flow rate can be controlled using a software.
Make: Custom
Details: Tube lens, light source, a fluorescence filters cube (Thorlabs TXRED MF559-34) which includes Texas Red filter set with emission (630 ± 34.5 nm) and excitation filters (559 ± 17 nm). A goniometer allows the setup to rotate to any orientations relative to gravity, a digital piezo controller (E-709.SRG, Physik Instrumente) controls the height of the objective (Olympus UPLFLN 20×) and a 3D printed piece holds the microslide sample.
Variable Angle Inspection Microscope allows for probing flow at any desired angle relative to gravity. The entire setup rotates such that the horizontal focal plane remains parallel to the substrate for all various orientations.
Snapshot of the result:
Publication:
Impact of resin molecular weight on drying kinetics and sag of coatings MW Issa, SV Barancyk, RM Rock, JF Gilchrist, and CL Wirth, accepted in Progress in Organic Coatings (2024)
Three-Dimensional Sag Tracking in Falling Liquid Films MW Issa, H Yu, MC Roffin, SV Barancyk, RM Rock, JF Gilchrist, and CL Wirth, accepted in Langmuir (2022)
Make: Zetasizer Nano ZS ZEN3600 (Malvern)
Details:
- Size range maximum (diameter): 0.3 nm to 10 µm
- Size range for Zeta potential (diameter): 3.8 nm to 100 µm
- Molecular weight range (Daltons): 342 Da to 28 × 107 Da
- Laser: 4mW 632.8nm ‘red’ laser
- Temperature range: 0 to 120 °C
- Particle size
The particle size measured in a Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) instrument is the diameter of the sphere that diffuses at the same speed as the particle being measured. The Zetasizer system determines the size by first measuring the Brownian motion of the particles in a sample using DLS and then interpreting a size from this using established theories.
- Molecular weight
The molecular weight of a substance is the weight in atomic mass units (amu) of all the atoms in one molecule of that substance. Mathematically the molecular weight can be calculated from the molecular formula of the substance; it being the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms making up the molecule.
- Zeta potential
Most liquids contain Ions; these are negatively and positively charged atoms called Cations and Anions respectively. When a charged particle is suspended in a liquid, ion of an opposite charge will be attracted to the surface of the suspended particle leading to a potential which varies according to the distance from the particle surface – this potential at the slipping plane is called the Zeta potential. Zeta potential is measured using a combination of the measurement techniques: Electrophoresis and Laser Doppler Velocimetry, sometimes called Laser Doppler Electrophoresis. This method measures how fast a particle moves in a liquid when an electrical field is applied – called Electrophoretic mobility. Once we know the velocity of the particle and the electrical field applied, by using two other known constants of the sample - viscosity and dielectric constant work out the zeta potential.
Snapshot of the result:
Size distribution for a capsule suspension measured using the Zetasizer. The result shows that the suspension includes components of three different size