Identifying epigenetic mechanisms underlying cardiac development
I am a doctoral trainee working in Dr. Kaixiang Cao’s lab. Our lab is interested in understanding how epigenetic events, including histone modifications, DNA modifications, and nucleosome positioning, impact cell fate. Also, how communication between different epigenetic pathways affect transcription, higher order chromatin architecture, and animal development. One primary area of interest is the role of histone modifiers in these processes.
My project aims to elucidate the role of epigenetic modifiers in the context of cardiac development. Previous research has implicated that epigenetic machineries are critical for heart development and in human cardiac pathologies. To further investigate the molecular mechanisms here, I am using embryonic stem cells and mouse models to explore the role of epigenetic modifiers in cardiac lineage specification. We will measure the impact of these enzymes on the regulation and expression of genes throughout cardiac differentiation and development using transcriptomic, genomic, and epigenomic tools such as scRNA-seq, ATAC-seq, and ChIP-seq. Deciphering the role of epigenetic regulation during cardiac development through functional genomics techniques promises to yield valuable information for treating congenital heart defects and heart failure.
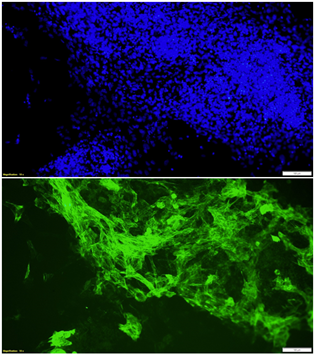
Top: Immunostaining with DAPI (blue) shows the nucleus of day 8 cardiomyocytes.
Bottom: Immunostaining of cardiac troponin T in day 8 cardiomyocytes.