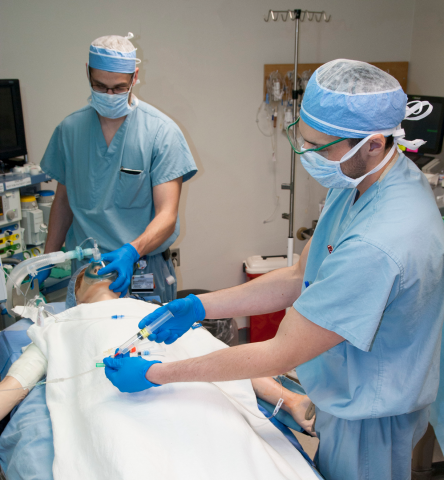
A peripheral nerve block is a type of regional anesthesia during which an anesthesiologist and anesthetist uses ultrasound to detect nerves in a person’s limb or extremity and administers medication directly to the nerves. This procedure “blocks” sensation to the area, numbing it and allowing for surgery. Patients who have received peripheral nerve blocks have reported short-term numbness, heaviness, weakness, or loss of muscle control in the intended region.
Peripheral nerve blocks allow for anesthesiologists and anesthetists to better control a patient’s pain during and after surgery, and to reduce reliance on oral narcotic pain medication. In many cases peripheral nerve blocks are less risk to a patient than general anesthesia. Additionally, patients who have received peripheral nerve blocks have reported less pain immediately following surgery and fewer side effects than those seen with general anesthesia. Ultimately, this technique enables patients to feel better faster.
Depending on the surgery needed, patients may remain awake throughout the procedure, may receive sedation, or may receive general anesthesia. The care plan is developed by the anesthesia care team, and is individualized for each patient.
Peripheral nerve blocks can be used in a variety of surgeries, and in many cases are delegated by anesthesiologists to anesthetists. It’s important for MSA students to learn the theory and technique, and to have opportunities for practice in both simulation and the clinical setting prior to entering the workforce.
Our Curriculum
The Master of Science in Anesthesia Program at Case Western Reserve University was the first program to actively train students how to perform peripheral nerve blocks on patients. Our curriculum incorporates didactic instruction, simulation training, and opportunities for clinical application.
A partner in this curriculum is the PNBschool, which was founded and led by a CWRU MSA alum Robert Thall, CAA. Thall teaches ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks to our first-year students in Cleveland, Houston, and Washington. He provides task trainers and ultrasound machines, which allow for students to put to practice the theory before attempting the procedure in the operating room.
Of the collaboration with PNBschool, Executive Director Joseph Rifici said, “We’re excited to partner with Bob Thall and the PNBschool to formerly train our students in the art of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blockade. The MSA Program at Case Western Reserve University recognizes the importance of proficiency in this area of anesthesia care, and we continue to strive to be the foremost educators of anesthesiologist assistants in the country.”
Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks have been used in operating rooms since the early 2000s, and are prevalent across the country. CWRU MSA students have been working with Thall to refine their technique in simulation training since 2016.
Learn more about our curriculum here.